More Paper Tube Manufacturers
Paper tubes, also known as cardboard tubes, are indispensable components across a wide range of industries, including food processing, shipping and postal services, automotive manufacturing, mechanical engineering, material handling, construction, textiles, the pulp and paper sector, packaging, healthcare, horticulture, and the arts. Their versatility, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness make them a preferred choice for businesses seeking reliable and eco-friendly packaging, transportation, and storage solutions.
The History of Paper Tubes
The evolution of paper tubes closely follows the historical progression of paper and cardboard. Paper itself originated in China, where, in 105 AD, Ts’ai Lun—an official in the court of Emperor Ho Ti—developed the first form of paper by pulping rags and fishing nets, later refining the process with plant fibers. The innovation spread through Asia and Europe, resulting in England’s first paper mill in 1495. Cardboard’s origins also trace back to China; by the 1600s, early forms of thick, durable cardboard were produced for packaging and protection.
The advent of modern paper tubes can be attributed to significant 19th-century advancements. In 1843, the invention of the wood grinding machine in Germany enabled paper manufacturers to efficiently create pulp from wood, accelerating both paper and cardboard production. This innovation paved the way for the creation of cardboard boxes, which are recognized as direct predecessors to paper tubes. The first pre-cut paper box, invented by Scottish-American Robert Blair in 1890, revolutionized packaging and shipping, notably improving the efficiency of transporting manufactured goods. By 1906, cardboard boxes had become a standard at the Kellogg factory, where they were used to package Cornflakes for mass distribution.
Paper tubes as we know them began appearing in London around 1903, where manufacturers started to design tube packaging for storage, protection, and as cores for winding fabrics, papers, and other flexible materials. Throughout the 20th century, ongoing advancements in material science, adhesives, and fabrication techniques enabled manufacturers to enhance the durability and versatility of paper tubes. The integration of waterproof linings and advanced adhesives expanded their use into more demanding applications, such as industrial packaging and the protection of sensitive products.
Today, the global demand for paper tube manufacturing continues to grow, driven by increasing awareness of environmental sustainability. Modern manufacturers emphasize recyclable and reusable solutions, and ongoing innovation is focused on developing biodegradable, compostable, and even reusable paper tube products. If you’re seeking ways to enhance your company’s sustainability profile or reduce packaging costs, consider exploring the latest developments in paper tube technology.
Are you curious about how paper tubes can improve your packaging workflow or help meet your sustainability goals? Learn more about paper tube applications and customization options here.
Paper Tube Design
Production Process
The manufacturing process for paper tubes begins with slicing large sheets of paperboard, cardboard, or kraft paper into narrow ribbons. These ribbons are coated with specialized adhesives before being wound around a mandrel. The orientation of the winding—either parallel or spiral—determines the tube’s final structure and performance characteristics. Spiral-wound tubes are the most common type due to their impressive combination of strength and cost-efficiency, making them suitable for everything from mailing tubes to heavy-duty industrial cores.
For applications requiring enhanced durability, such as mailing, shipping, or industrial storage, manufacturers may add multiple layers of material to increase wall thickness and strength. Interior linings, often made from waterproof or grease-resistant materials, can be incorporated to protect contents from moisture, humidity, or chemical exposure. The tubes are then cured in ovens to ensure the adhesive fully bonds the layers, resulting in a finished product that resists deformation, crushing, and environmental stressors.
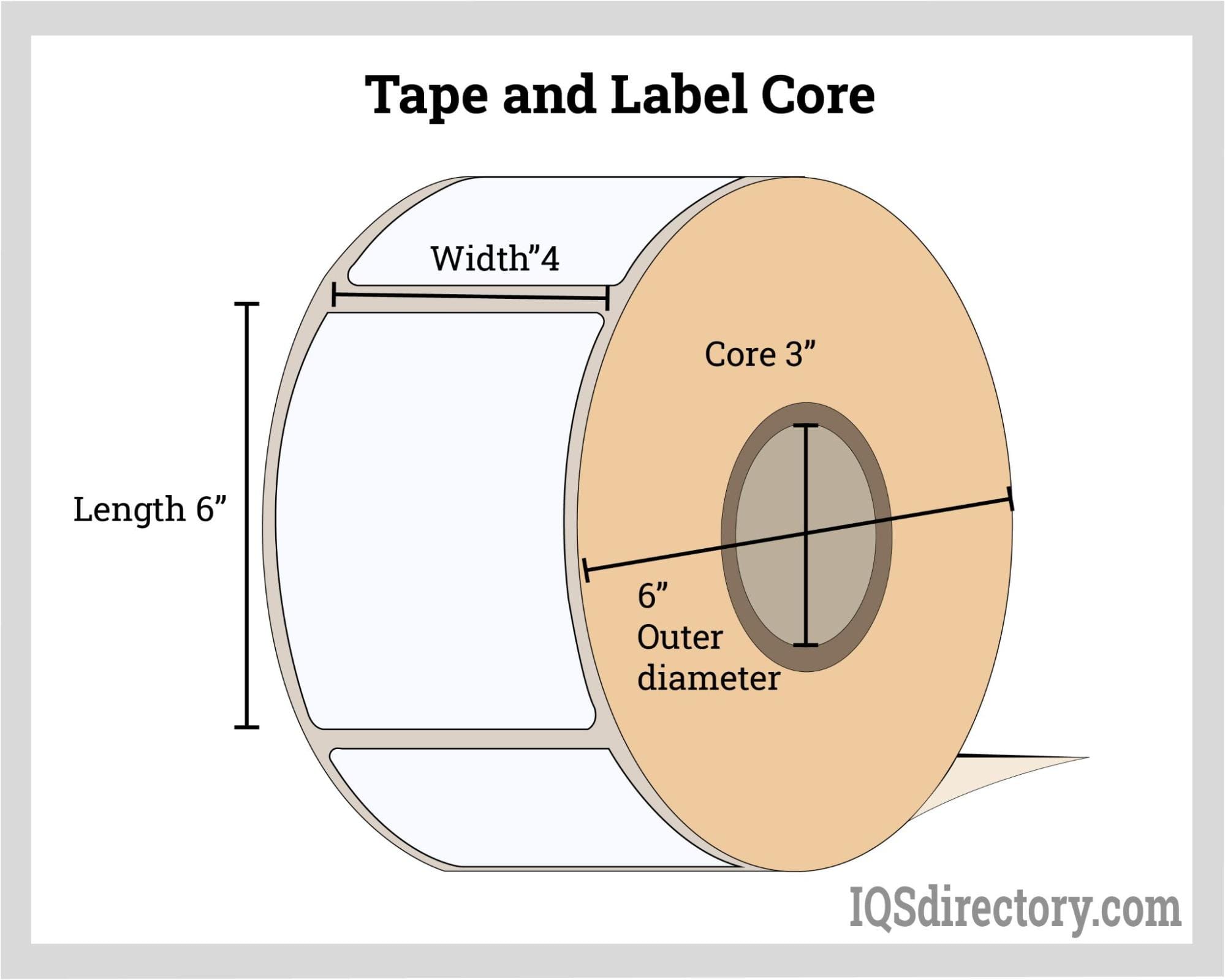
Paper tubes are measured and classified according to their internal diameter, wall thickness, and length. These dimensions are critical not only for ensuring the tube’s strength and load-bearing capacity but also for compatibility with automated packaging equipment and end-user requirements.
Materials
Paper tubes are engineered from a selection of high-strength, sustainable, and versatile materials. Common options include:
- Kraft paper: Known for its strength and natural resistance to tearing, kraft paper is ideal for packaging and shipping tubes that require durability.
- Cardboard: Used widely for general-purpose tubes, cardboard provides an optimal balance between cost, strength, and recyclability.
- Recycled paper: Many manufacturers use post-consumer recycled fibers to minimize environmental impact and support eco-friendly packaging initiatives.
- Paperboard and fiberboard: These denser materials are chosen for heavy-duty applications, such as industrial cores, concrete form tubes (sonotubes), and protective packaging.
- Waterproof or water-resistant cardboard: Enhanced with resins, coatings, or laminated linings, these tubes are designed for use in high-humidity environments or where moisture resistance is critical.
- Paper-adhesive composites: Special blends incorporating advanced adhesives offer increased load-bearing strength and flexibility for demanding applications.
Choosing the right material depends on your specific application, environmental requirements, and desired level of protection.
Considerations and Customization
Custom paper tube design requires careful consideration of the application, protection requirements, tube dimensions, and branding preferences. Key factors include:
- Functionality: Is the tube intended for mailing, storage, product display, or as a structural core?
- Strength and durability: What level of resistance is needed against crushing, denting, or environmental exposure?
- Dimensions: Required internal diameter, length, and wall thickness must be tailored to the product and handling needs.
- Protection: For delicate, fragile, or sensitive items, thicker walls and water-resistant linings are recommended.
- Branding and aesthetics: Custom printing, colored coatings, decorative foils, and unique finishes help reinforce brand identity, especially for retail and gift packaging.
- Closure options: End caps, plugs, and tamper-evident seals can be specified for added security and product integrity.
Manufacturers regularly collaborate with clients to develop tailored solutions, ensuring that every custom paper tube meets the intended use case and enhances the overall customer experience.
Paper Tube Features
Paper tubes, sometimes interchangeably called cardboard tubes, are cylindrical structures formed by tightly winding and gluing multiple layers of paper or paperboard. The result is a hollow, lightweight, yet exceptionally strong tube capable of serving numerous functions across industries. The key features of paper tubes include:
- High strength-to-weight ratio for efficient shipping and storage
- Customizable sizes, wall thicknesses, and lengths for diverse applications
- Wide range of material options, including recycled and eco-friendly choices
- Ability to incorporate protective linings, coatings, and branding elements
- Secure closure options with end caps, plugs, or fold-in ends
- Compatibility with a variety of automated packaging and handling systems
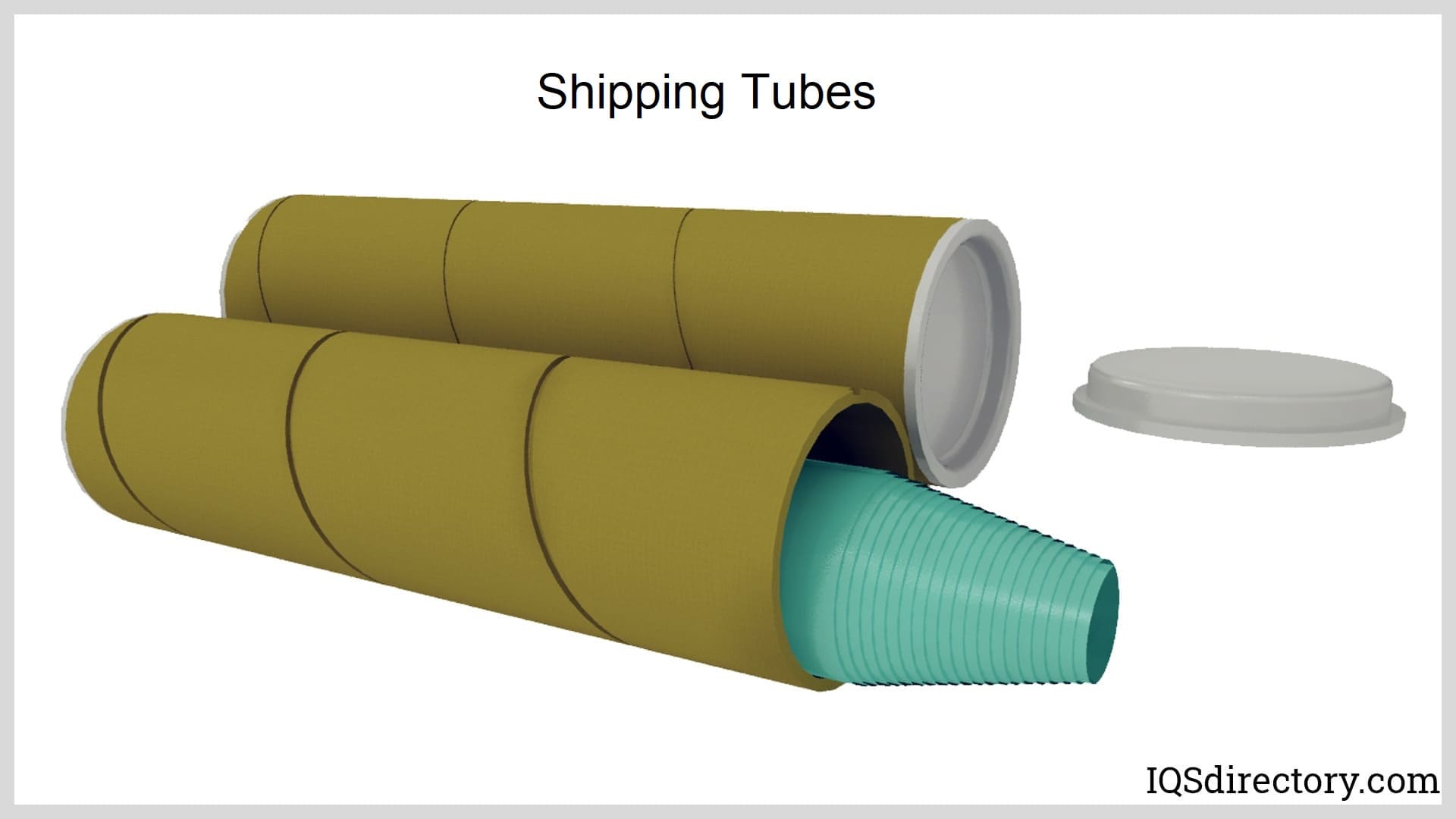
For mailing and shipping, shipping tubes are often fitted with plastic or metal end caps, safeguarding contents like blueprints, artwork, sensitive documents, and medical specimens. Some designs utilize fold-over ends, while others offer tamper-evident closures for added security in transit.
Are you interested in learning which tube features are best suited to your product or shipping requirements?
Types of Paper Tubes
The diversity of paper tube designs reflects their broad utility across many sectors. Common types include:
- Paper cores: These robust tubes provide structural support for winding and storing materials such as toilet paper, paper towels, textiles, electrical wires, tape, and even industrial lubricants. They are often specified by their end-use, like “toilet paper cores” or “fabric roll cores.”
- Shipping tubes (Mailing tubes): Designed to protect rolled items—from posters and blueprints to certificates and artwork—during shipping or storage. Their rigid construction defends against bending, crushing, or moisture damage.
- Kraft tubes: Fabricated from premium kraft paper, these tubes offer exceptional durability and resilience, making them ideal for postal applications and high-impact shipping scenarios.
- Caulking tubes: Essential in construction and building maintenance, caulking tubes are spiral-wound and engineered to dispense sealants or adhesives through caulking guns. Their design ensures clean, efficient application and prevents leakage.
- Sonotubes: Heavy-duty cylindrical forms used by contractors to mold and shape concrete columns, pillars, or supports in construction projects. Sonotubes are engineered to withstand the pressures of wet concrete and facilitate easy removal once cured.
- Paper cans: Versatile containers used for packaging dry foods, snacks, powdered beverages, cosmetics, and specialty products. Paper cans offer an attractive, protective, and eco-friendly alternative to metal or plastic canisters.
- Protective packaging tubes: Custom-designed tubes for protecting sensitive electronic components, glassware, or specialty devices during shipment and storage.
Advantages of Paper Tubes
Paper tubes offer multiple benefits that make them a preferred packaging and storage solution for businesses and consumers alike:
- Eco-friendly and sustainable: Most paper tubes are made from recycled materials, and their recyclability supports circular economy initiatives and reduces landfill waste. Many manufacturers also offer compostable or biodegradable options for further environmental impact reduction.
- Cost-effective: Compared to metal, plastic, or glass alternatives, paper tubes are less expensive to produce, purchase, and dispose of, making them an economical choice for high-volume applications like mailing, packaging, and industrial use.
- Customizable for a wide range of uses: Whether you need a tube for product packaging, document shipping, retail display, or construction, paper tubes can be tailored to meet your exact requirements in terms of size, strength, and appearance.
- Lightweight yet durable: Despite being light, paper tubes can be engineered to provide significant resistance to denting, crushing, and impact, protecting valuable or sensitive contents throughout the supply chain.
- Easy to handle and store: Their cylindrical shape makes them stackable and space-efficient, while also enabling efficient use in automated handling and packaging lines.
- Versatility of closure and accessory options: With a variety of end caps, plugs, and seals, paper tubes can be adapted to protect contents from moisture, tampering, or accidental opening.
It’s important to note that while paper tubes are generally strong and flexible, their natural porosity means that additional linings or coatings may be necessary for applications involving moisture-sensitive or perishable goods, such as food or pharmaceuticals. For electrical wiring or high-value electronics, non-conductive and moisture-resistant barriers can be incorporated for enhanced protection.
Industries making extensive use of paper tubes include food processing, automotive, textiles, material handling, construction, logistics, horticulture, healthcare, pulp and paper, mechanics, and the creative arts.
Paper Tube Accessories
To maximize performance and extend the useful life of paper tubes, a range of accessories and enhancements are available:
- Sealants and coatings: Waterproof, grease-resistant, or UV-protective coatings improve resistance to moisture, chemicals, and sunlight, making tubes suitable for demanding environments.
- End caps, plugs, and seals: Plastic, metal, or paperboard end caps secure tube contents, preventing spillage, contamination, or accidental opening. Tamper-evident options are recommended for sensitive or high-value shipments.
- Custom printing and labeling: Enhance product visibility and brand recognition with full-color graphics, barcodes, or QR codes directly printed on the tube surface.
- Protective linings: Liners made from foil, waxed paper, or polymer films provide an additional barrier against moisture, aroma transfer, or oxygen ingress—especially important for food and pharmaceutical packaging.
- Handles and carrying straps: For larger or heavier tubes, ergonomic handles simplify transport and improve user convenience.
Properly selected accessories enhance tube performance, extend product shelf life, and create a premium impression for end-users.
Curious about which accessories can add value to your packaging?
Proper Care for Paper Tubes
Although paper tubes are durable, following proper care and storage guidelines will help extend their lifespan and maintain the integrity of stored or shipped items:
- Storage: Store tubes vertically whenever possible to prevent bending, flattening, or crushing over time. Avoid stacking heavy objects on top of horizontally stored tubes. Ensure storage areas are dry, well-ventilated, and free from excessive humidity. If moisture cannot be avoided, consider protective plastic wrapping or waterproof coatings to shield the tubes.
- Protection from pests: Cardboard and adhesives can attract insects or rodents. Store tubes in sealed containers or pest-free environments. Regularly inspect for signs of infestation and treat storage spaces as needed.
- Handling and usage: Always handle tubes with care, especially during loading and unloading. Avoid exposing them to rain, snow, or direct sources of heat, as paper tubes are flammable and susceptible to water damage. For outdoor use, select weather-resistant or coated tubes to mitigate environmental risks.
- Disposal and recycling: When a tube reaches the end of its useful life, recycle it according to local guidelines. Many tubes are compostable or biodegradable, further supporting sustainability initiatives.
Looking for more tips on storing and handling your paper tubes?
Paper Tube Standards
Quality, safety, and sustainability standards for paper tubes vary depending on their intended application and industry requirements. Key compliance factors include:
- Food contact safety: Tubes used for food packaging must meet FDA guidelines and, in some cases, NSF International certification for hygiene and contaminant resistance.
- Sustainability certifications: Look for suppliers certified by the Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI), Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), or equivalent programs, ensuring responsible sourcing and manufacturing practices.
- Material quality: ASTM International standards outline specifications for paper tube strength, thickness, and performance, helping ensure tubes meet rigorous quality benchmarks.
- Industry-specific regulations: Sectors like healthcare, electronics, and hazardous goods may require additional certifications for chemical resistance, anti-static properties, or tamper-evidence.
Working with a reputable manufacturer ensures compliance with relevant standards, giving you peace of mind regarding product safety and performance.
Have questions about certification or regulatory requirements for your paper tubes? Contact an industry-certified manufacturer today.
Choosing the Right Paper Tube Manufacturer
Selecting the ideal paper tube manufacturer is crucial for achieving the best combination of product quality, customization options, supply consistency, and value for money. Consider the following factors when evaluating potential partners:
- Customization capabilities: Can the manufacturer accommodate your specifications for size, strength, material, and branding?
- Certifications and compliance: Does the supplier comply with applicable standards and offer documentation for quality, safety, and sustainability?
- Production scale and lead times: Are they equipped to fulfill your volume requirements within your desired timelines?
- Reputation and experience: Does the manufacturer have a proven track record in your industry? Can they provide references or case studies?
- Pricing and value-added services: Are their products competitively priced, and do they offer additional services such as design consultation, prototyping, or logistics support?
We maintain a curated list of top paper tube manufacturers, each vetted for quality, reliability, and industry expertise. Ready to start your search? Browse our recommended paper tube manufacturers and request a quote today.
For additional resources and a deeper dive into the world of cardboard packaging, check out our Cardboard Tubes website. Here you’ll find comprehensive information on cardboard tube types, manufacturing techniques, and application guides to help you make the most informed purchasing decisions.
Still have questions or need guidance on your next paper tube project? Contact our experts for tailored advice and solutions.
What are paper tubes and where are they commonly used?
Paper tubes, also known as cardboard tubes, are hollow cylindrical structures made by winding paper or cardboard layers. They are widely used in industries such as food processing, shipping, automotive, textiles, packaging, healthcare, construction, and the arts due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
How are paper tubes manufactured?
Paper tubes are manufactured by slicing sheets of paperboard or kraft paper into ribbons, coating them with adhesives, and winding them around a mandrel in either a spiral or parallel orientation. Layers are added for strength, and tubes are cured in ovens to solidify the adhesive bond.
What materials are used to make paper tubes?
Common materials for paper tubes include kraft paper, cardboard, recycled paper, paperboard, fiberboard, waterproof or water-resistant cardboard, and paper-adhesive composites. The choice of material depends on application requirements, durability needs, and desired sustainability.
What types of paper tubes are available?
There are several types of paper tubes, including paper cores for winding materials, shipping and mailing tubes, kraft tubes, caulking tubes, sonotubes for concrete forms, paper cans for packaging food and specialty products, and protective packaging tubes for fragile or sensitive items.
What are the key benefits of using paper tubes?
Paper tubes offer eco-friendliness, recyclability, cost-effectiveness, customizability for various uses, lightweight durability, easy handling, and a wide range of closure options. They support sustainability initiatives and can be engineered for specific strength and protection requirements.
How do I properly care for and store paper tubes?
Store paper tubes vertically in dry, well-ventilated areas away from excessive humidity. Avoid stacking heavy objects on them, protect them from pests, handle them carefully, and use water-resistant coatings or wrapping if moisture exposure is possible. Recycle or compost used tubes per local guidelines.
What standards and certifications should I look for in paper tubes?
Look for FDA food contact compliance, sustainability certifications like SFI or FSC, ASTM standards for strength and thickness, and any industry-specific requirements for safety or chemical resistance. Reputable manufacturers provide certification and comply with relevant quality benchmarks.
What factors should I consider when choosing a paper tube manufacturer?
Consider the manufacturer’s ability to customize tube sizes, materials, and branding; their compliance with industry standards; production capacity and lead times; reputation and experience; and additional services such as design support or logistics. Choose a vetted supplier for quality and reliability.








 Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard Tubes Carrying Cases
Carrying Cases Contract Packaging
Contract Packaging Corrugated Boxes
Corrugated Boxes Dot Peening Machines
Dot Peening Machines Labeling Machinery
Labeling Machinery Marking Machinery
Marking Machinery Packaging Equipment
Packaging Equipment Palletizers
Palletizers Plastic Bags
Plastic Bags Sewing Contractors
Sewing Contractors Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services